This Sept. 16 and 17 is the next meeting of the Federal Open Markets Committee begins, investors, economists, and policymakers are trying to predict how the central bankers will react to a weakening labor market and stubborn unemployment.
Fed watchers expect the central bank’s policy committee to cut its influential federal funds rate for the first time since December.
Traders are pricing in a 96% chance that central bankers will cut the rate by a quarter of a point, to 4%-4.25%, according to the CME Group’s FedWatch tool, which forecasts rate movements based on fed funds futures trading data.
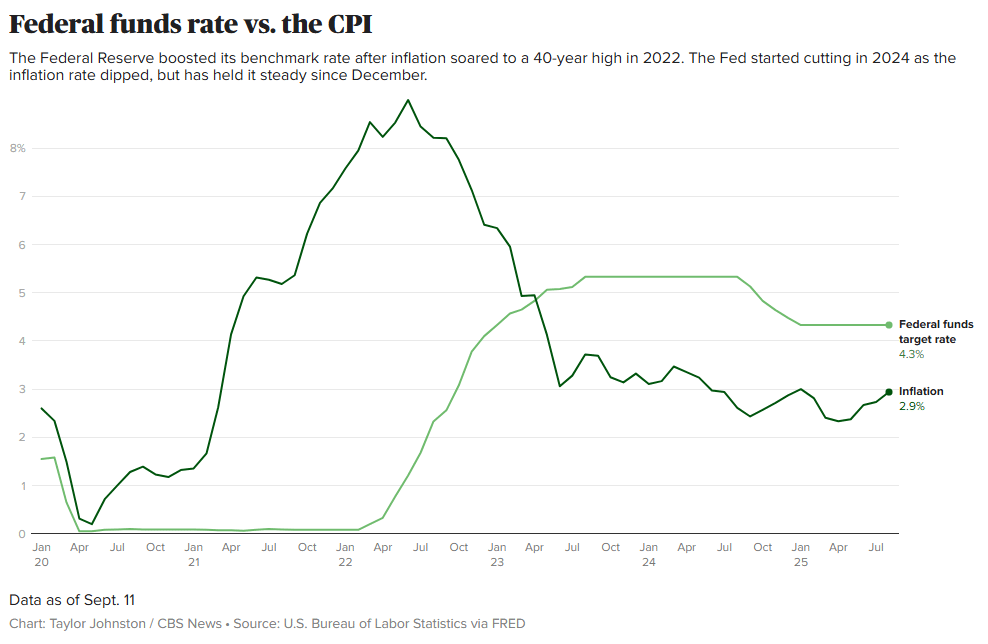
Since insurance companies invest the premiums they receive mainly in bonds and other fixed-income assets so when rates drop annuity rates usually fall as well.
If you’re eyeing a Multi-Year Guaranteed Annuity (MYGA) for retirement security, timing matters. If rates are rising then sometimes it is best to stick out, decreasing rates insinuate a annuity rate drop.
Today’s Annuity Rate Snapshot: Still Holding Strong Pre-Cut Even with a rate cut on the horizon, fixed annuity rates remain elevated compared to last year, fueled by lingering high bond yields. Insurers are investing premiums in fixed-income securities, so they can still offer competitive MYGA yields.
Today's Top Annuity Rates by Duration
Get Your Free Annuity Quote | Looking for specifics? 3-Year Rates | 7-Year Rates | 10-Year Rates
How are Annuity Rates Determined?
Annuity are determined by a mix of economic factors and insurer strategies. At their core, they’re fixed rates guaranteed for a set term (e.g., 3-10 years), allowing your principal to grow tax-deferred without market risk.
- Interest Rate Environment: When Treasury yields or the federal funds rate rise annuities tend to follow along shortly.
- Inflation and Economic Growth: Higher inflation expectations push rates up to maintain real returns. In 2023-2025, rates surged from 2-3% lows (2020-2022) to 6%+ peaks amid post-pandemic recovery.
- Insurer Factors: Competition, portfolio risk management, and financial strength (e.g., AM Best ratings) influence offerings. Stronger carriers might offer slightly lower but more stable rates.
- Types of Annuities: MYGAs lock a fixed rate for the full term; fixed indexed annuities tie to market indices with caps; variable annuities fluctuate with investments.
Pro Tip: Rates aren’t just about the highest number—factor in liquidity (e.g., 10% free withdrawals) and taxes. Use our calculator to see how deferral boosts after-tax growth.
Annuity Rate Forecast for 2025
We predict that annuity rates will begin to decrease in the very near term. Based on historical patterns we would not expect to see a decrease greater than what is announced atfter the FOMC Rate Meeting tonight.
Top 5-Year MYGA Rates (Most Popular Term)
| Term | Insurer | Annuity | Rate | AM Best | Apply |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 Years | Knighthead Life | Staysail Annuity | 6.45% Simple | A- | Apply |
| 5 Years | Mountain Life | Alpine Horizon | 6.15% | B+ | Apply |
| 5 Years | Revol One | DirectGrowth MYGA | 5.85% | B++ | Apply |
| 5 Years | Nassau | MyAnnuity | 5.75% | B++ | Apply |
| 5 Years | Farmers Life | Safeguard Plus | 5.60% | B++ | Apply |
Example: $100,000 at 6.45% simple interest earns $6,450 annually (before taxes). Rates subject to change; guarantees backed by issuer’s claims-paying ability.
Annuities vs. CDs: Post-Fed Cut Edition
A rate cut hits savers hard, but annuities’ tax deferral gives them an edge. Use our quick comparison (assuming a 32% tax bracket):
| Feature | Fixed MYGA Annuity | Bank CD |
|---|---|---|
| Top 5-Year Rate (Sept 2025) | 6.45% (tax-deferred) | 5.40% (taxed annually) |
| After-Tax Effective Yield | ~6.45% compounds pre-tax | ~3.67% (post-tax compounding) |
| Liquidity | 10% free annual withdrawal | Early penalty (3-6 months interest) |
| Protection | Insurer + state guaranty | FDIC up to $250k |
| Fed Cut Impact | Lags; holds higher longer | Drops immediately |
Run the Numbers: For $100k over 5 years, a MYGA at 6.45% nets ~$36,500 gain (pre-tax). Same CD? ~$24,800 after taxes. Try Our Calculator
When to Buy:
- Lock Now If: You're 55+ and need guaranteed income by 2030—rates won't rebound quickly.
- Wait If: You expect rates to bottom out (unlikely soon) or prefer shorter terms for flexibility.
- Ladder Strategy: Split into 3/5/7-year MYGAs to capture today's highs and future resets.
Pro Tip: Use a 1035 exchange to swap old annuities tax-free into hotter rates.