What is an IRA Annuity?
An IRA Annuity is an investment product that combines two powerful financial tools, an IRA (Individual Retirement Account) and an annuity. An annuity is a contract between an individual and an insurance company that provides a stream of guaranteed payments for a specific period or a lifetime.
An IRA is a retirement account that allows individuals to save and invest money in a tax-advantaged way. The combination of these two products results in an investment vehicle that offers tax-deferred growth and a steady stream of income during retirement.

How Does an IRA Annuity Work?
An IRA is a tax-advantaged retirement account that allows individuals to save money for their retirement years. The money in the account grows tax-free. Individuals can invest in a wide range of financial products, such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
Traditional IRAs allow individuals to deduct their contributions from their taxes, while Roth IRAs offer tax-free withdrawals in retirement.
An IRA annuity is a type of IRA that allows individuals to purchase an annuity contract within their IRA account. An IRA annuity can be either a traditional annuity or a Roth annuity, depending on the type of IRA account.
With a traditional IRA annuity, the contributions are made with pre-tax dollars, and the payments are taxed as income when withdrawn. With a Roth IRA annuity, the contributions are made with after-tax dollars, and the payments are tax-free.

Are IRA Ditributions Taxable?
Traditional IRAs
Any deductible contributions and earnings you withdraw or that are distributed from your traditional IRA are taxable. Also, if you are under age 59 ½ you may have to pay an additional 10% tax for early withdrawals unless you qualify for an exception.
Roth IRAs
You do not pay taxes on withdrawals from a Roth IRA Annuity if it is a qualified distribution (or a withdrawal that is a qualified distribution). Otherwise, part of the distribution or withdrawal may be taxable. If you are under age 59 ½, you may also have to pay an additional 10% tax for early withdrawals unless you qualify for an exception.
IRA Annuity Distribution Rules 2023
Withdrawals from an IRA annuity are subject to specific rules that govern the timing and amount of the payments. The IRS requires you to take RMDs at age 73, or face a penalty. The amount of the distribution is determined based on the individual’s age, account balance, and life expectancy.
Withdrawals from an IRA annuity are subject to ordinary income taxes, regardless of whether they come from a traditional or Roth IRA annuity. If an individual withdraws money from a traditional IRA annuity before age 59 ½, they may face a 10% penalty in addition to income taxes.
Contributions made to a Roth IRA can be taken out tax-free whenever needed, yet the profits may be taxed and fined if taken out before 59 ½ years old or inside the first 5 years of the account.
Pros and Cons of IRA Annuities
There are several advantages and disadvantages of IRA annuities. several advantages, they also have some drawbacks that individuals should consider before investing. Based on our research, we’ve compiled the below pros and cons of IRA annuities list.
Pros
Tax-Deferred Growth: One of the biggest advantages of an IRA annuity is that it allows for tax-deferred growth. With a traditional IRA, contributions are tax-deductible, and the money grows tax-free until it is withdrawn. However, with an IRA annuity, the tax-deferred growth continues even after the required minimum distributions (RMDs) start at age 73, allowing the funds to grow and compound over time.
Guaranteed Income: An IRA annuity provides a guaranteed stream of income for life or for a specified period. This makes it an ideal investment option for retirees who are looking for a secure source of income that they cannot outlive. The annuity’s payout rate is determined at the time of purchase, and the payments continue regardless of market conditions.
Flexibility: IRA annuities offer a high level of flexibility. They can be customized to meet an individual’s specific needs, including selecting the payout rate, the length of the payment period, and any additional features like a death benefit or inflation protection.
Protection Against Market Volatility: An IRA annuity provides protection against market volatility. Unlike traditional investments like stocks and bonds, the annuity’s payout rate is fixed, and the payments continue even if the market takes a downturn.
Estate Planning: An IRA annuity can also be used as a tool for estate planning. Some annuity products allow for the transfer of the annuity contract to a beneficiary after the annuitant’s death. This allows for the continuation of the annuity’s payout to the beneficiary.
Inflation Protection: An IRA annuity with an inflation protection rider can provide an increase in the payout rate to help keep up with the rising cost of living.
Cons
High fees: IRA annuities can be more expensive than other investment products, and the fees can eat into the returns over time.
Limited investment choices: An IRA annuity may limit the investment choices available to individuals, which can be a disadvantage for those who want more flexibility in their investment strategy.
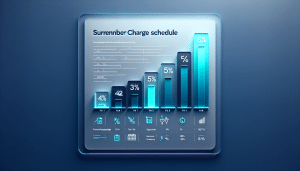
Surrender charges: Many annuities have a surrender charge. This fee is charged by the insurance company if the individual withdraws money from the annuity within a specific period. The period is typically between 5-10 years.
Complexity: Annuities can be complex financial products, and individuals may need to work with a financial professional to understand the terms and features of the annuity contract fully.
Inflation risk: Annuity payments may not keep up with inflation over time, which can reduce the purchasing power of the payments during retirement.
IRA Contribution Limits 2023
2023 IRA contributions can’t be more than:
- $6,500 ($7,500 if you’re age 50 or older), or If less, your taxable compensation for the year*
The IRA contribution limit does not apply to:
- Rollover contributions
- Qualified reservist repayments
*Roth IRA and traditional IRAs combined.
Roth IRA Income Limits 2023
This table shows whether your contribution to a Roth IRA is affected by the amount of your modified AGI as computed for Roth IRA purpose.
How do You Calculate Modified AGI?
If the amount you can contribute must be reduced, figure your reduced contribution limit as follows.
- Start with your modified AGI.
- Subtract from the amount in (1):
- $218,000 if filing a joint return or qualifying widow(er),
- $-0- if married filing a separate return, and you lived with your spouse at any time during the year,
- $138,000 for all other individuals.
- Divide the result in (2) by $15,000 ($10,000 if filing a joint return, qualifying widow(er), or married filing a separate return and you lived with your spouse at any time during the year).
- Multiply the maximum contribution limit (before reduction by this adjustment and before reduction for any contributions to traditional IRAs) by the result in (3).
- Subtract the result in (4) from the maximum contribution limit before this reduction. The result is your reduced contribution limit.
See Publication 590-A, Contributions to Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs), for a worksheet to figure out your reduced contribution.