
Best 7 Year Fixed Annuity Rates 2025
Lock in today's best 7 year fixed annuity rates, defer taxes, and buy your annuity at home - all through one independent platform.
- A-Rated Carriers
- Independent & Unbiased
- Secure Quote Process
- No Sales Pressure
Highest 7 Year Fixed Annuity Rates Preview
- Wichita National Security 7*6.10%
- Revol One DirectGrowth 7*6.00%
- Sentinel Security Personal Choice*5.90%
*Illustrative snapshot. Click below for live updates & full comparison including carrier strength, liquidity, and renewal options.
View Full ComparisonRates subject to change without notice. Availability & features vary by state and insurer. Guarantees are backed by the claims‑paying ability of the issuing insurance company. Not a bank product. Not FDIC insured. State guaranty association limits apply (vary by state).
Best 7 Year Fixed Annuity Rates
7 year fixed annuity rates are guaranteed for the entire length of the contract term. Fixed annuities are often referred to as “CD-type” annuities because of their similarities to a certificate of deposit. Annuity rates are issued by an insurance company rather than the bank, and the issuing insurance company sets its own annuity rates.
How 7 Year Fixed Annuities Work
7-year fixed annuity rates are guaranteed for 7 years. Insurance companies issue annuities, and product features vary by insurance company and from product to product. Many fixed annuities allow you to take free withdrawals of your interest or up to 10% of your annuity’s account value each year.
How interest is credited
Most annuities earn interest daily and credit the interest to the annuity account value each month. More than 90% of all fixed annuities use compound interest, which means you earn interest on top of your interest. However, recently, a handful of annuity companies have begun to offer fixed annuities that credit using simple interest.
Annuities that use simple interest only pay interest on your original deposit and not on the interest you earn; these types of annuities are best for someone who plans to withdraw their interest each month (compounding doesn’t matter in this case).
Taxes: Qualified and Non-Qualified Funds
- Withdrawal taxation: All withdrawals are taxed as ordinary income, as neither the contributions nor the growth has been taxed yet.
- Early withdrawal penalty: If you withdraw funds before age 59½, you may face a 10% early withdrawal penalty from the IRS, in addition to paying ordinary income taxes.
- Withdrawal taxation: Only the earnings portion of a withdrawal is taxed as ordinary income. The part of the withdrawal that is a return of your original, after-tax contributions (your “basis”) is tax-free.
- LIFO taxation: The IRS applies a Last-In, First-Out (LIFO) rule to non-qualified annuities. This means that for withdrawals or surrenders, the earnings are considered to come out first and are taxed as ordinary income, before your tax-free contributions are returned.
- Early withdrawal penalty: Similar to qualified annuities, non-qualified annuities are subject to a 10% early withdrawal penalty on the taxable earnings portion if you make withdrawals before age 59½.
Liquidity and penalty-free withdrawals
Not all fixed annuities offer the same liquidity or free-withdrawal provisions, so it is important to look closely at these features when comparing annuities. Each annuity will offer one of these three options:
- No free-withdrawals
- Free withdrawals of interest
- 10% free withdrawals (10% of annuity account value)
You also want to consider when the free withdrawals become available. Some annuities make free withdrawals available in year one, while other products don’t allow for any withdrawals until year 2.
Surrender Charges and Early Withdrawal Rules
Typical 7 Year Annuity Surrender Schedule
A surrender charge is applied to any withdrawal during the 7 year annuity contract that is not allowed by a free withdrawal provision (i.e., interest only, 10% free). Surrender charges in annuities tend to be fairly steep, so it is cruicial to consider your liquidity needs before purchasing an annuity.
A typical surrender charge schedule is 9% in Year 1, 8% in Year 2, 7% in Year 3, 6% in Year 4, 5% in Year 5, 4% in Year 6, and 3% in Year 7.
At the end of the 7 year contract, you can renew for another 7 years, transfer your annuity to another insurance company using a tax-free 1035 exchange, or take possession of all of your funds without penalty.
Market Value Adjustment (MVA) explained
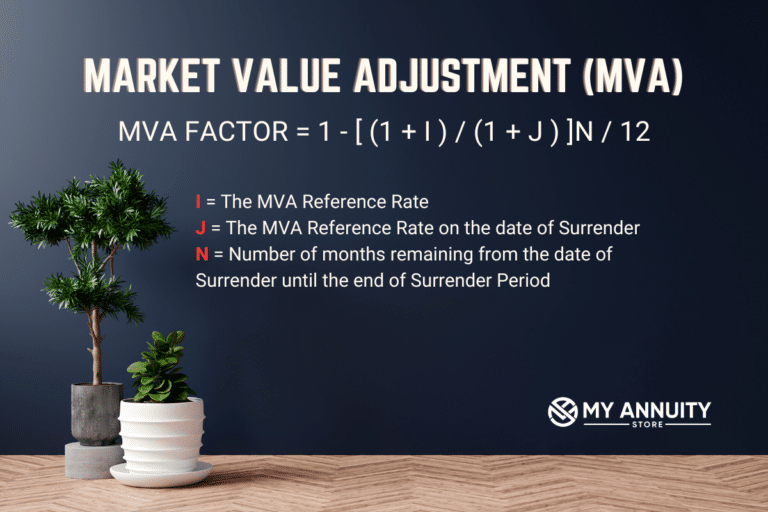
An MVA adjusts the value of an early withdrawal based on changes in a specific interest rate index. If interest rates have risen since the annuity was purchased, the MVA will likely be a negative adjustment, decreasing your payout; if rates have fallen, it will be positive, increasing it.
The MVA is typically only applied to withdrawals that exceed any penalty-free limits or to the entire contract if surrendered before the end of a surrender period.
10% Free Withdrawals & When They Reset
10% free withdrawals are a fairly common feature among 7 year fixed annuities; fixed annuity rates are often less for annuities with 10% free withdrawals than it is for annuities with no liquidity.
The way it works is you are allowed to withdraw up to 10% of your previous year’s account value. You are allowed to take the 10% free withdrawal once per annuity contract year.
59½ Rule and IRS Penalties
The “59½ rule” is an IRS guideline that imposes a 10% pernalty on withdrawals from an annuity before age 59½. This applies to accounts like 401(k)s, 403(b)s, and traditional IRAs.
Fixed Annuity vs. Bonds. vs. CDs
Which Fits Your Safety and Income Goals?
- Fixed Annuity (MYGA)
- Pros: Guaranteed rate for the term, tax-deferred growth, optional lifetime income features, typically higher yields than comparable CDs.
- Cons: Surrender charges/limited liquidity, insurer credit risk (mitigated by state guaranty associations; not FDIC), potential penalties/taxes on early withdrawals before 59½.
- Best for: Savers seeking predictable growth and tax deferral, and those open to converting assets into future income.
- Certificates of Deposit (CDs)
- Pros: FDIC insurance up to limits, simple and predictable interest, and short to medium terms available.
- Cons: Interest taxed annually, early withdrawal penalties, often lower yields than top MYGAs.
- Best for: Short-term cash needs, emergency reserves, and ultra-conservative savers prioritizing FDIC backing.
- Bonds (Treasuries, corporates, munis)
- Pros: Broad choice of durations/credits, tradable before maturity, potential tax advantages (e.g., munis), Treasuries carry full faith and credit of the U.S.
- Cons: Market price can fluctuate with interest rates and credit risk, coupons generally taxed annually (except munis), and reinvestment risk.
- Best for: Investors comfortable with market movement and want income and flexibility, or specific tax planning via munis.
- Quick contrasts
- Safety backstop: CDs = FDIC; MYGAs = insurer guarantees + state guaranty associations; Bonds = issuer/market risk (Treasuries are the highest credit quality).
- Taxes on growth: MYGAs defer until withdrawal; CDs and most bonds tax interest annually.
- Liquidity: Bonds are tradable (price risk); CDs/MYGAs penalize early access (MYGAs often allow up to 10% free withdrawals annually).
- Income options: Only annuities can convert to lifetime income; CDs and bonds provide interest only.
More CD vs. Annuity Content

Fixed Annuity vs CD Calculator
Fixed Annuity vs. CD vs. Bonds Comparison Guide
Disclosures: Guarantees are backed by the issuing insurer’s financial strength and claims-paying ability. CDs are FDIC insured up to limits. Bonds are subject to interest rate and credit risk. This is educational, not individualized advice.
Who Should Consider a 7 Year Fixed Annuity?
- Pre-retirees 5–10 years out: Want a guaranteed rate while closing in on retirement without stock market swings.
- Savers looking for higher yield than CDs: Comfortable locking funds for 7 years and want a higher rate that CDs offer.
- Risk-averse investors: Prefer principal protection, predictable growth, and tax-deferred interest over market volatility.
- People with a defined timeline: Know they won’t need this chunk of money for at least 7 years (college, retirement, home payoff horizon).
- Tax-sensitive savers: Want tax-deferred growth to potentially reduce current-year taxable interest compared to CDs/bonds in taxable accounts.
- Ladder builders: Using a 3–5–7–10 year ladder to smooth reinvestment risk and capture rates over time.
- Rollover money: IRA/401(k) rollovers seeking a safe, set-it-and-forget-it allocation inside a retirement account.
- Income planners: Plan to annuitize or do penalty-free withdrawals after year 1 to supplement income within carrier rules.
- Those needing simplicity: Prefer a straightforward, fixed rate and clear surrender schedule with minimal moving parts.
- Investors in states with solid guaranty association coverage: Appreciate state-level protection backstops subject to limits and rules.
Quick Cautions:
- Early withdrawals above the free-penalty amount can trigger surrender charges and potential tax penalties if under 59½.
- The issuing insurance company sets the rates and can change for new contracts; lock before rate changes if timing is critical.
- Always confirm state availability, free-withdrawal percentage, and AM Best/financial strength before purchase.
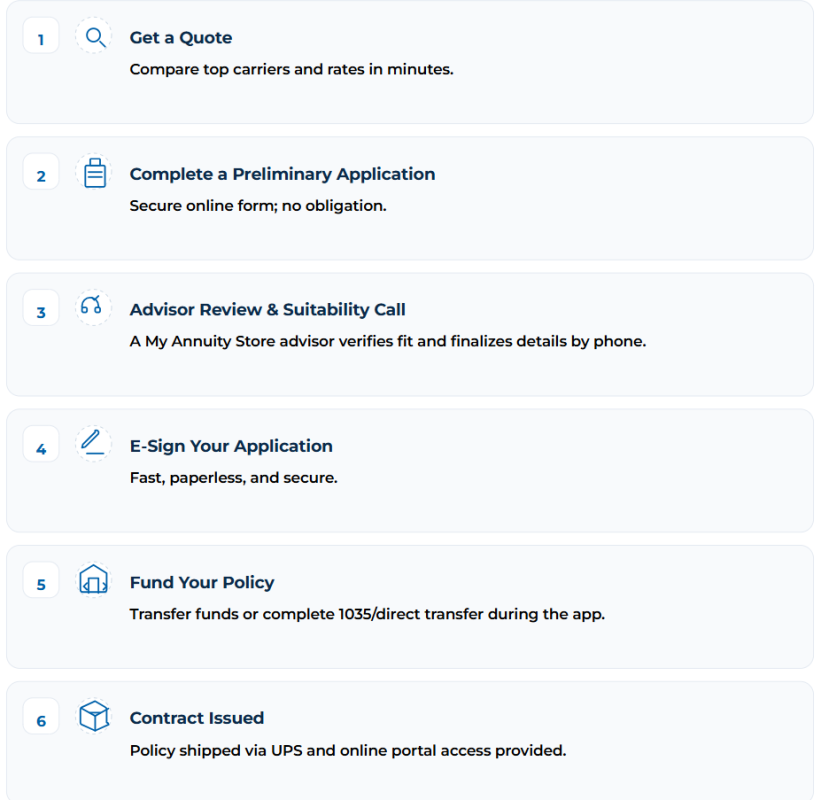
How to Buy an Annuity Online at My Annuity Store
Annuity Guides
As Seen On:






