Best Fixed Index Annuity Rates for February 2026
- Last Updated: February 2, 2026
- Jason Caudill, MBA
Fixed Index Annuity Rates Table
When evaluating fixed index annuity rates, it’s crucial to compare the different options available to maximize your retirement income. Fixed Index Annuities credit interest based on the performance of an external stock market index, such as the S & P 500 or the Nasdaq. Interest is credited to the annuity when the value of the market index goes up. When the market index goes down, no interest is credited.
If you are looking for fixed annuity rates, you can find them here instead.
| Product Name | Company Name | AM Best | Max Age | Minimum | Years | Income Rider | Free withdrawals | Pt-to-Pt Cap | Premium Bonus | Fixed Rate | Learn More |
|---|
Compare the Best Fixed Index Annuity Rates Today
Many investors are currently interested in fixed index annuity rates for their potential benefits.
The table below lists the fixed index annuity rates and crediting strategies for the top fixed index annuities available today. Click the compare button to compare up to 3 annuities side by side.
When comparing different options, take note of the fixed index annuity rates available to you.
| Compare | Carrier | AM Best / S&P | Product | Indexing Strategies (Highlights) | Current Caps & Rates | Surrender Schedule | Min Guarantee | State Availability | Min Premium | Issue Ages | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MassMutual Ascend | A++ / A+ | WealthChoice 7 (Single) | Fixed Rate 1-Year S&P 500 Annual Pt-to-Pt Cap Horizon Ascent 5% Index Pt-to-Pt Participation 1-Year S&P 500 Performance Trigger Additional strategies available • FireLight eligible | Fixed: 8.00% S&P 500 Pt-to-Pt Cap: 10.25% Horizon Ascent 5% Par: 165.00% Perf Trigger: 7.10% | 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3 (7 yrs) | 87.5% of premium @ 1.00% | Except: AK, HI, ME, NY | $20,000 | 0–90 | Cap Bailout (S&P 500) 6.75%; 10% free W/D yr 1; TI/NH waivers; Income rider (with cost, max issue age 75 with GLBR); Non-MVA in AK, PA, UT (lower caps/rates); CA higher caps/rates, no MVA; E-Application only; Rate/Cap decrease noted 10/27. | |
| Nationwide Life Ins. Co. of America | A+ / A+ | American Legend 7 (Flexible) | Fixed Rate S&P 500 Annual Pt-to-Pt Cap S&P 500 7-Year Cap Lock Pt-to-Pt S&P 500 RC Pt-to-Pt Participation Additional strategies available • FireLight eligible | <$100k / $100k+ Fixed: 4.05% / 4.25% S&P 500 Cap: 9.50% / 10.00% 7-Yr Cap Lock: 7.00% / 7.25% RC Participation: 70.00% / 75.00% | 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3 (7 yrs) | 87.5% of premium @ 3.00% | Except: NY | $10,000 (NQ / Q); add-ins $2,000 | 0–85 (NQ/Q) | 10% free W/D yr 1; LTC/Confinement & TI waivers (varies by state); Additional premium in 1st year only; CA surrender/rate variations. | |
| Delaware Life | A- / A- | Peak 10 (Single) | Fixed S&P 500 Avg DRC Ann Pt-to-Pt Cap AB Growth & Value Bal Par (2-Year) J.P. Morgan Cycle Par (2-Year) S&P 500 Avg DRC Par (2-Year) Additional strategies available | <$100k / $100k+ Fixed: 3.70% / 3.95% Avg DRC Cap: 8.50% / 9.50% AB G&V Par (2-Yr): 220% / 240% JPM Cycle Par (2-Yr): 235% / 250% Avg DRC Par (2-Yr): 195% / 205% | 10, 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2 (10 yrs) | 1.00% on 87.5% of premium | Except: CA, DE, NY | $25,000 | 0–85 | Guaranteed Income Solution included (no fee); Bonus Income+ Rider (with fee); State variations for surrender & rates/caps; LTC/Confinement & TI waivers (varies). | |
| MassMutual Ascend | A++ / A+ | WealthChoice 5 (Single) | Fixed Rate 1-Year S&P 500 Annual Pt-to-Pt Cap Horizon Ascent 5% Index Pt-to-Pt Participation 1-Year S&P 500 Performance Trigger Additional strategies available • FireLight eligible | Fixed: 7.00% S&P 500 Pt-to-Pt Cap: 10.25% Horizon Ascent 5% Par: 160.00% Perf Trigger: 7.00% | 9, 8, 7, 6, 5 (5 yrs) ± MVA | 90.8% of premium @ 3.85% | Except: NY | $25,000 | 0–90 | Cap Bailout (S&P 500) 6.50%; 10% free W/D yr 1; TI/NH waivers; Flexible premium in year 1; E-Application only; Rate/Cap decrease noted 10/27. | |
| Sagicor | A- | Sage Accumulator 5 (Single) | 1-Year Fixed 1-Year S&P 500 Annual Pt-to-Pt Cap 1-Year Pt-to-Pt MSCI EAFE ETF Par 1-Year Pt-to-Pt MSCI Emerging Market Par Additional strategies available • FireLight eligible | <$75k / $75k+ Fixed: 4.50% / 5.00% S&P 500 Cap: 9.50% / 10.50% MSCI EAFE Par: 60% / 65% MSCI EM Par: 55% / 60% | 9, 8, 7, 6, 5 (5 yrs) ± MVA | 87.5% of premium @ 1.00% | Except: AK, HI, ME, NY | $20,000 | 0–90 | 10% free W/D yr 1; TI/NH waivers; CA different rates & surrender charges. | |
| Sagicor | A- | Sage Accumulator 7 (Single) | 1-Year Fixed 1-Year S&P 500 Annual Pt-to-Pt Cap 1-Year Pt-to-Pt MSCI EAFE ETF Par 1-Year Pt-to-Pt MSCI Emerging Market Par Additional strategies available • FireLight eligible | <$75k / $75k+ Fixed: 4.50% / 5.00% S&P 500 Cap: 9.50% / 10.50% MSCI EAFE Par: 60% / 65% MSCI EM Par: 55% / 60% | 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3 (7 yrs) ± MVA | 90.8% of premium @ 3.85% | Except: NY | $250,000 | 0–90 | 10% free W/D yr 1; TI/NH waivers; CA different rates & surrender charges. | |
| Delaware Life | A- / A- | True Path Income (Single) | 1-Year S&P 500 Annual Pt-to-Pt Cap 1-Year S&P 500 Pt-to-Pt w/ Performance Trigger Fixed Rate Additional strategies available • FireLight eligible | <$100k / $100k+ S&P 500 Cap: 5.00% / 5.50% Perf Trigger: 4.50% / 5.00% Fixed: 3.10% / 3.35% | 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 (10 yrs) ± MVA | 87.5% of premium (less w/d & related charges, excl. MVA) @ 2.65% | Except: NY | $25,000 (add-ins $500 NQ) | 45–85 | 30-day free withdrawal/surrender window at end (or prior, if applicable) of guarantee period. |
Popular Indexes and Strategy Types
- S&P 500: Classic, widely understood baseline
- Volatility-Control Indexes (e.g., proprietary bank indexes): Smoother paths; often higher participation rates
- Multi-Asset Blends: Diversified rules-based indexes with dynamic volatility management
- Strategy Types:
- Annual Point-to-Point with Cap
- Annual Point-to-Point with Participation (No Cap)
- Annual Point-to-Point with Spread (No Cap)
- Monthly Sum/Monthly Average (less common today)
- 2-Year Strategies (may offer higher terms with longer reset)
Investors should carefully consider fixed index annuity rates when choosing a strategy that fits their financial goals.
Indexes Available in Fixed Index Annuities
Fixed index annuity rates are influenced by various factors including market conditions and contract terms. The variety of fixed index annuity rates available today allows for tailored investment strategies.
How Fixed Index Annuities Work
Market trends can influence fixed index annuity rates, making research essential.
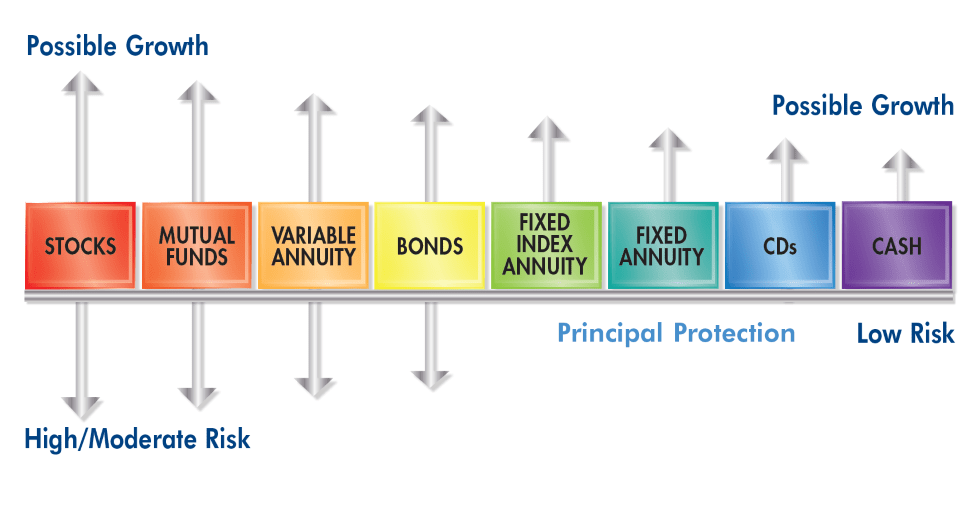
Principal Protection
Principal protection linked to fixed index annuity rates provides peace of mind for investors.
- Your premium is not invested directly in the market.
- You cannot lose principal due to index performance (market downturns don’t reduce your base).
Index-Linked Growth
Choosing the right index can affect your fixed index annuity rates and overall returns.
- Interest credits are calculated based on an index method chosen each reset period.
- Carriers set caps, participation rates, or spreads—these can change at each renewal but not retroactively for completed terms.
Tax-Deferred Accumulation
Consider how fixed index annuity rates will impact your long-term financial strategy.
- Interest grows tax-deferred inside the contract.
- Withdrawals are taxed as ordinary income; early withdrawals may incur penalties.
Fixed index annuity rates can provide a safety net while allowing for potential growth.
Liquidity and Surrender Charges
Understanding surrender charges can help investors navigate fixed index annuity rates more effectively.
- Typical surrender schedules: 5, 7, or 10 years.
- Most contracts include 10% free withdrawals annually after the first year.
- Surrender charges and market value adjustments (MVA) may apply to excess withdrawals.
How are Fixed Index Annuity Rates Calculated?
The fixed index annuity rates determine your potential earnings over the investment period. The choice between caps, participation, and spreads is crucial when analyzing fixed index annuity rates.
Cap Rate
Fixed index annuity rates vary by provider, so it’s important to compare options.
- The maximum annual interest credit for a capped strategy.
- Example: If the S&P 500 returns 12% and your cap is 7%, your credit is 7%.
Participation Rate (Par)
Monitoring your fixed index annuity rates can lead to better financial outcomes.
- You receive a percentage of the index gain with no explicit cap.
- Example: If par is 45% and the index returns 12%, credit is 5.4% before any spreads or fees.
Spread (Margin)
Fixed index annuity rates can provide a balanced approach to growth and security.
- A fixed percentage subtracted from the index gain.
- Example: If spread is 3% and the index returns 10%, your credit is 7%.
Pro tip: Often, volatility-control indexes pair with higher participation rates, which can be attractive in today’s rate environment.
Top Fixed Index Annuity Companies & Notable Features
Read our Comprehensive Best Fixed Index Annuity Companies of 2026 Guide to learn more about the product offerings from top rated insurance companies.
- Allianz: Multiple Income Rider options and increasing income options.
- Athene: Offers many unique volatility-controlled indexes with uncapped crediting strategies.
- Nationwide: Income riders guarantee the highest income payments at many ages.
Fixed Index Annuity FAQs
Are fixed index annuity rates fixed?
No. Fixed index annuity (FIA) crediting terms—caps, participation rates, and spreads—are declared by the carrier and can change at each renewal period. Once a term is completed, that credit is locked in and cannot be retroactively changed.
Can I lose money in a fixed index annuity?
Your principal and credited interest are protected from market losses. However, your contract value can decrease if you take withdrawals above the free-allowance, surrender early (surrender charges/MVA may apply), or if you pay optional rider fees.
How often do you update FIA rates?
We aim to refresh this page monthly and whenever carriers release significant rate changes. For the most current carrier-approved rate sheets, call 855-583-1104 or email info@myannuitystore.com.
What’s the difference between a cap, participation rate, and spread?
- Cap: The maximum annual interest credit for a capped strategy.
- Participation rate (par): The percentage of the index gain you receive, often with no explicit cap.
- Spread: A fixed percentage subtracted from the index gain before crediting interest.
Example: If the index returns 12% and your cap is 7%, your credit is 7%. If par is 45%, credit would be 5.4% before any spreads. If spread is 3% and the index returns 10%, credit is 7%.
Do fixed index annuities have fees?
Many accumulation-focused FIAs have no explicit annual policy fee. Optional riders (e.g., lifetime income, enhanced death benefit) may carry fees that reduce your contract value. Always review the product disclosure for details.
What liquidity do FIAs offer?
Most FIAs include free withdrawals (often up to 10% of the account value annually) after the first contract year. Withdrawals above the free amount during the surrender period may incur surrender charges and a market value adjustment (MVA), if applicable.
Which indexes and strategies are most popular?
Common choices include the S&P 500 and proprietary volatility-control indexes from major banks. Popular strategies include Annual Point-to-Point with a cap, participation rate (no cap), or spread, plus occasional 2-year strategies that may offer different terms.
Is a fixed index annuity better than a MYGA?
It depends on your goals. MYGAs offer a guaranteed multi-year fixed rate and simplicity. FIAs provide principal protection with index-linked growth potential, but credits vary by terms and index performance. If guaranteed rate is the priority, a MYGA may fit; if growth potential above a fixed rate appeals—with protection—consider an FIA.
How do I choose the right FIA?
Match the surrender period to your time horizon, confirm liquidity needs, and select a mix of strategies and indexes that align with your risk tolerance. If lifetime income is a goal, compare rider fees, roll-up rates, and payout factors in addition to accumulation terms.
How can I get personalized recommendations?
Call 855-583-1104 or email info@myannuitystore.com. We’ll confirm your state, objectives, and liquidity needs, then share carrier-approved rate sheets and best-fit products.
Fixed Indexed Annuities vs Fixed Annuities (MYGAs)
When comparing products, fixed index annuity rates should be a key consideration.
- FIA: Principal protection, index-linked growth potential, variable annual interest credits
- MYGA: Guaranteed multi-year fixed rate; simpler, no index decisions
- Fixed (Traditional): Annual declared rate; typically more conservative Tip: If guaranteed rate is the priority, see our current MYGA rates page. If growth potential above a fixed rate appeals to you—with protection—FIA may fit.
Fixed index annuity rates may offer attractive options compared to traditional products.
Things to Consider
There are many aspects to consider regarding fixed index annuity rates that could impact your decision.
Available Indexes: The stock market indexes available in the index annuity. We have a list of available stock market indexes available at each insurance carrier for simplicity.
Duration: Typically, the longer contract you purchase the higher your guaranteed interest rate will be. But that is not the case, especially given the current inverted yield curve.
Liquidity: Most all fixed annuities have some type of annual free withdrawals available, but the amount available varies by product. You’ll see most of the fixed annuities at our marketplace provide interest-only withdrawals annually. Others allow for 10% Free Withdrawals (10% of the previous year’s account value) annually.
Insurance Company’s Financial Rating: It is very important to consider an insurance company’s financial rating because it is an indicator of its ability to fulfill financial commitments to its policyholders. Usually, a lesser-rated insurance company will offer higher fixed annuity rates, but that is not always the case.